Biomedicine struggles how to account for specificity and complexity when addressing mechanisms of disease. Diseases are neither just local nor just systemic.
- Non-steroidal NR subtype agonists
- Non-steroidal NR subtype antagonists
- Tissue selective NR subtype agonists
- Nuclear receptor reprogramming (NRRP) drugs
Female physiology is closely regulated by hormone fluctuations regulated by their associated NRs.
Estrogen Receptor Selective Modulation
Our current focus is on the development of drugs for the treatment of selective estrogen receptor modulating drugs for indications such as menopausal hot flashes, Alzheimer’s disease, Vaginal atrophy, PCOS, endometriosis and autoimmune disorders.
Cancer Cell Metabolism – the Warburg Effect
Cancer cells rely primarily on glycolysis rather than oxidative phosphorylation, even in the presence of oxygen. Aerobic glycolysis is advantageous to cancer cells because it is an efficient mode for energy production where the tumor micro-environment has less access to both oxygen and glucose. We are developing oxidative glycolysis inhibitors.
Endocrine Resistant Breast Cancer
60-75% of breast cancers contain estrogen receptors (ER) and are classified as ER+ tumors. 30% of localized ER+ tumors do not respond to tamoxifen; de novo resistance. Over 50% of tumors that initially responded to tamoxifen develop acquired resistance. We are developing BIM modulators for endocrine resistant tumors.
Pipeline of Drugs
| Drug | MOA | Indication |
|---|---|---|
| MF5 | Selective ERβ agonist | Menopause vasomotor symptoms |
| AZ1 | ER NRRP (nuclear receptor reprogramming) | Alzheimer Disease |
| BZ2 | Oxidative Glycolysis Inhibitor | Triple negative Breast Cancer |
→ MF5 is expected to enter Phase 1 clinical trials in early 2026
All other drugs are in various pre-clinical stage of development.
MF5
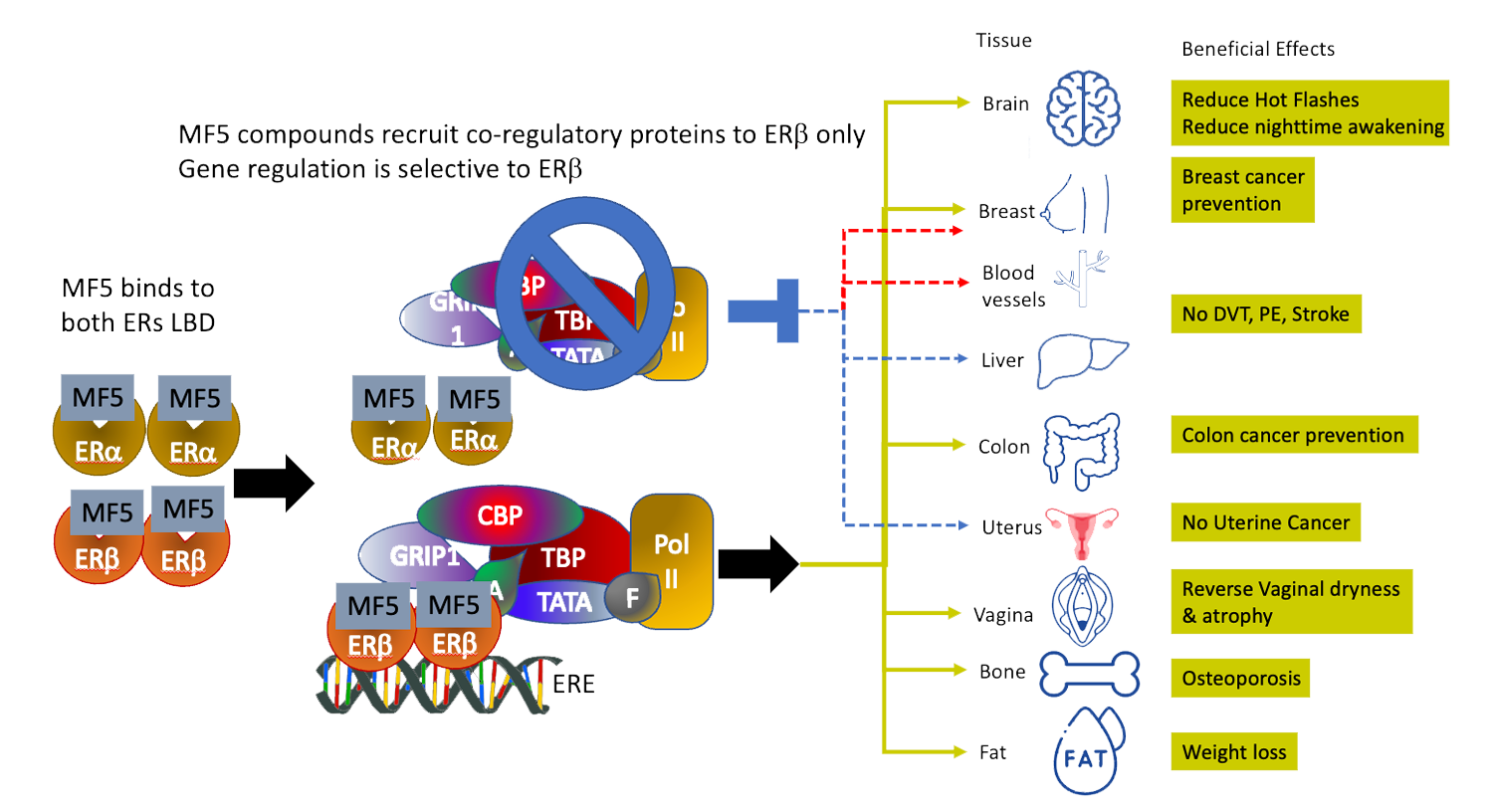
- MF5 is an estrogen receptor β-selective agonist small molecule optimized from statistically significant Phase 2 results of MF101, a botanical under FDA IND.
- MF5 is designed to treat menopausal symptoms including hot flashes while preventing breast cancer.
- MF5 is also designed to not increase the risk of uterine cancer and clotting encountered with menopause hormone therapy.
AZ1
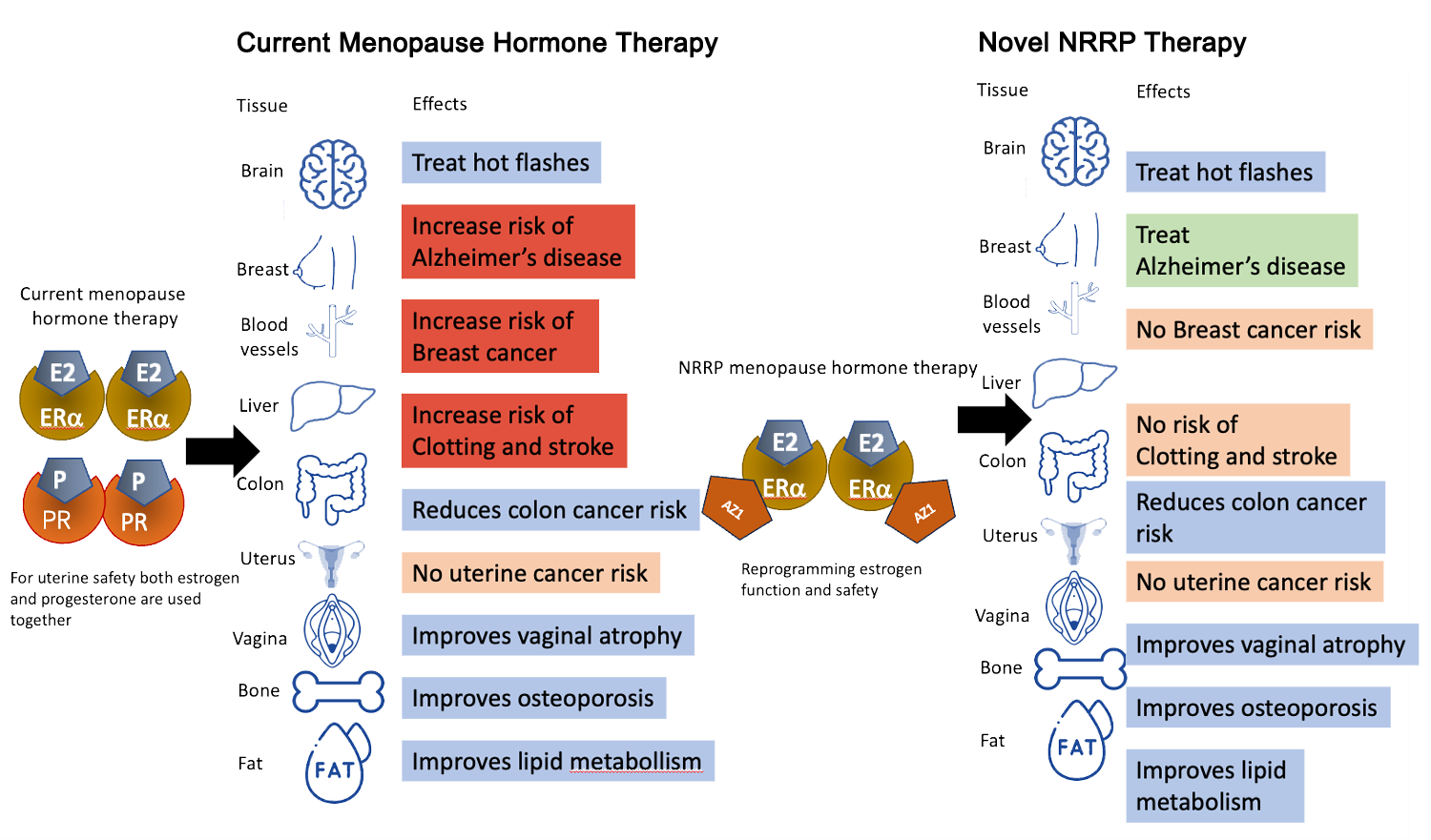
- AZ1 is nuclear receptor reprogramming (NRRP) drug.
- AZ1 is delivered with estrogen used in current menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) formulas.
- AZ1 blocks estrogen from activating oncogenes.
- AZ1 also causes estrogens to regulate a new set of genes.
- AZ1 plus estrogen results in neuroprotective effect and can be taken safely for many years.
BZ2
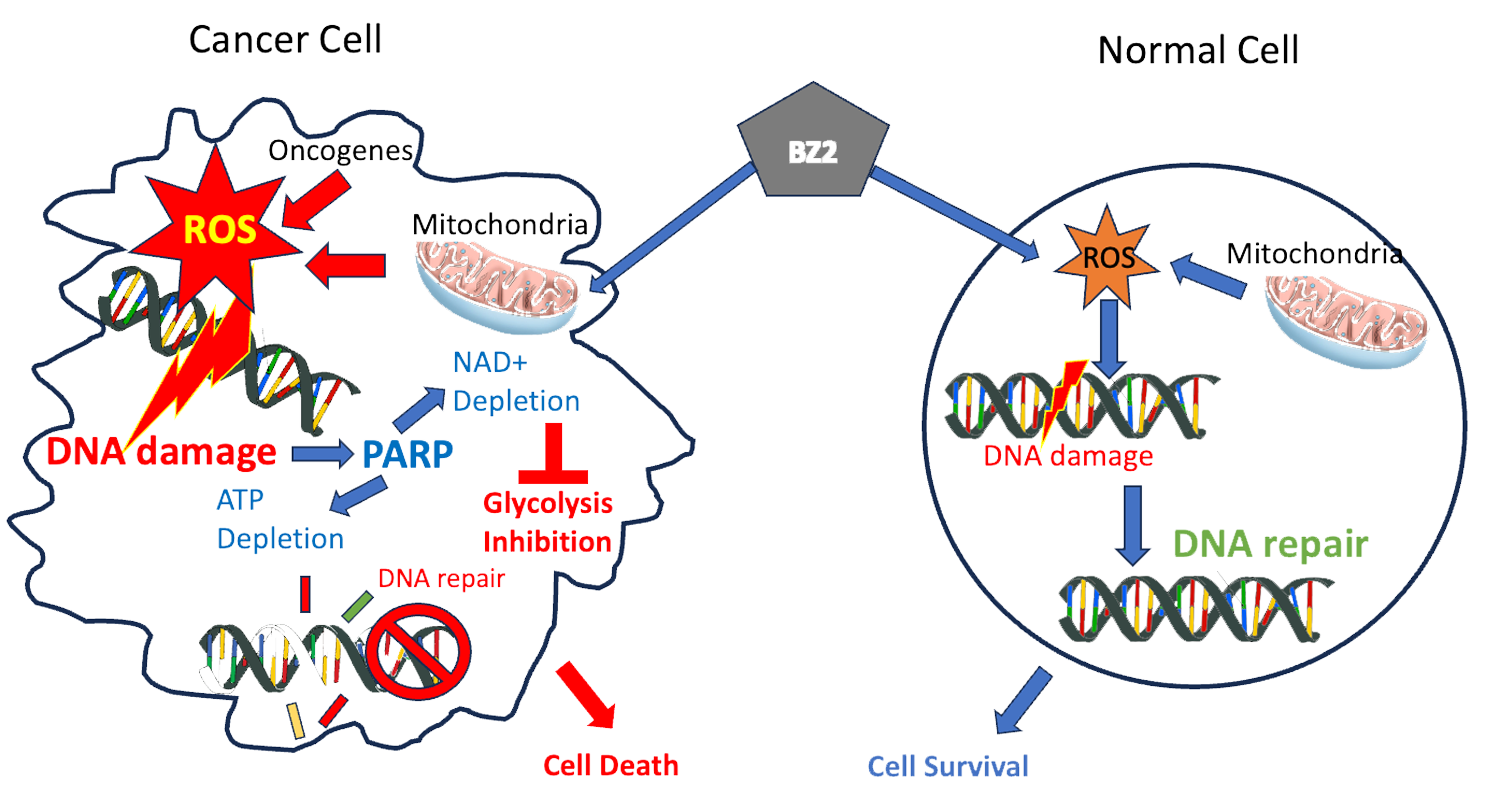
- BZ2 is an oxidative glycolysis inhibitor small molecule optimized from BZL101, a botanical under FDA IND.
- BZ2 is designed to treat solid tumors.
- BZ2 results in selectively inducing cancer cells death while sparing normal cells.
- Oxidative DNA damage induces activation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase PARP. PARP is involved in DNA damage repair
- BZ2 depletes cellular NAD+/H and ATP selectively in cancer cells.
- Lactate secretion (measure of glycolytic activity) and glycolytic enzymes are inhibited in cancer but not normal cells.